Real time learning for credit card fraud detection
Credit card fraud is a term for theft or fraud committed using a payment card, such as a credit card or debit card, as a fraudulent source of funds in a transaction. Although they only correspond to almost 0.1% of all transactions, these frauds result in huge financial losses (It was estimated as approx. $0.07 loss for every $100 of transaction). Currently all the banks are using different Machine learning pipelines to detect these fraudulent transactions. However, it is identified that even most sophisticated methods are unable to identify many of the false transactions.

One of the main reason for this misclassification is because of the change in fraudulent behavior from time to time. This shows that the past data on which the models are built are not effective for predicting the current frauds. All the existing Machine learning pipelines involves training in batch modes on sets of data, but as the fraud behavior changes in real time they reduce the predictability power of models. Also, it is necessary for the models to have the flexibility to delete the effects of very old transaction data. All these emphasizes the need for ongoing training of machine learning models and the real learning models.
ARTML for Fraud detection
Artml - Simple yet most powerful real time learning technique can be used in detecting frauds to minimize the misclassifications. With its capacity to build models in real time and also with the power of real time feature selection and model rebuilding it can help decrease the fraud prediction misclassifications. Using artml we can train the models as we get the freshest labelled data and hence incorporate the real time behavior of the fraudulent. Let us see how we can use artml for predicting fraud detections in real time. Code for this real time pipeline is provided in this Jupyter notebook
Data preparation
Labelled Card transactions data gathered in real time can be preprocessed and feature engineering can be performed as required. Suppose if the dataset is having high dimensional features then even PCA can be applied in real time (use PCA function in artml library). For this blog post example, Credit Card Fraud Detection dataset from the Kaggle is used. (In the jupyter notebook explanation Two Credit Card Fraud Detection datasets are used for better explaining the artml library)
Data Exploration
Real time univariate & bivariate statistics for the data can be obtained using the artml functions. Current dataset is having 28 features (obtained after performing PCA). As discussed before, the dataset is highly unbalanced accounting 492 frauds out of 284,807 transactions. (the positive class (frauds) are 0.172% of all transactions)
Modeling
Linear discriminant analysis (LDA model) which gives good accuracies in most of the binary classification problems is chosen for making predictions about the fraud. LDA Model is imported from artml library and trained with the data. Code
In all the traditional ML approaches feature selection is done when the model is initially built combined with the domain knowledge. But as time progresses there might be some new variables which are significant for credit default prediction. The reason is that fraud behavior changes timely, and defaulters come up with new strategies every time to avoid the wrong transactions being caught. Therefore, features in the model needs to be updated in real-time to improve the predictability power.
Conventional ML approaches lack the true power of feature selection because model cannot be updated to consider new set of features time to time. Using artml we can use the existing model for selecting the best features and then update the model based on these new features to make better predictions. this process is continuous and model gets upgraded every time to always make better decisions.
We are performing feature selection using Lda model, precisely by calculating mahalanobis distance for different features in predicting the target. Read documentation to know more about how to implement this.
Model Evaluation
The accuracy of the basic model is 99.91% even without any feature engineering. But, as the dataset is highly unbalanced this metric can be totally misleading. Since the dataset accommodates only 492 frauds out of 284,807 transactions, implies by even predicting every transaction to be fair we can achieve an overall accuracy of 99.828% accuracy.
Also, when feature selection is performed it shows that the accuracy of 99.91% can be achieved only by using two out of 28 features (using less features also improves the computation speed).
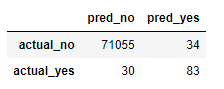
Above Confusion matrix for the model shows that still there are 30 cases where the model is unable to detect the fraud behavior. We can reduce this by varying precision recall threshold values.
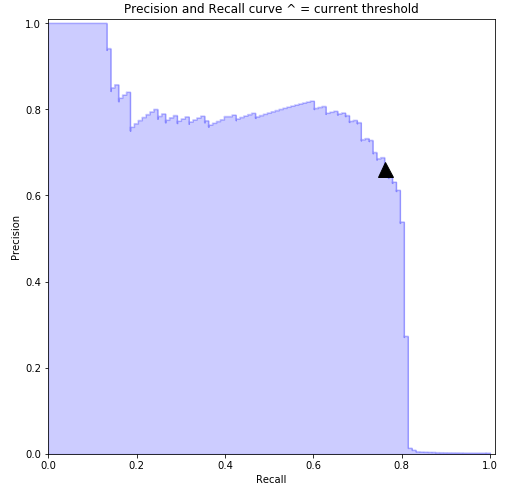
Above precision recall threshold curve shows that we can achieve a maximum recall of about 75-77% by maintain precision to be around 77-78%. This implies that we can predict almost 75-77% fraud transactions out of all frauds. And out of the predicted fraud cases almost 77-78% of transactions will be real frauds. Also, the models AUC (Area under curve) is found to be 0.89 which shows the predictive power of the model.
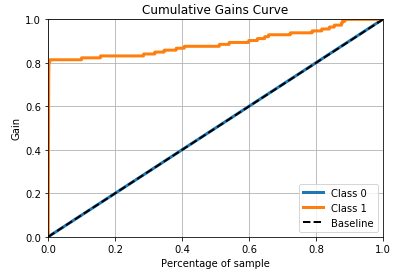
The model performance can be further improved when new features are created with feature engineering techniques combined with domain knowledge.
Deployment in Real-time
As the new labelled data gets generated, the model performance can be improved by training the model with new data and by deleting the effects of old data in the model in real time. Learn and forget functions in artml library helps to update BET in real time with the data. Once the BET table gets updated then the model is automatically upgraded on the fly. Also, artml library has the power to incorporate and delete certain features in the model in real time. As we are updating the effect of new data into the model we can perform real time feature selection using artml and hence update the model with new features whenever required. Although we can use Forget and Learn functions for training model with data in real time, what data to be added to the model and what data needs to be deleted should be decided based on domain knowledge and also by checking model performance Use learn, forget, grow, delete and feature selection functions from artml library for performing these tasks.
Discussion
All the steps mentioned above can be automated in a pipeline which makes the process self-sustaining. This mentioned framework is applied only on a sample Kaggle dataset. We look forward to apply this in real scenario on a Big data. The model and tasks can be built even better for each specific Business case making it more powerful. Contact us for any Industrial consultations.