ARTML API Explanation- Iris dataset
ART-ML library with its simple architecture can update the models in real time using the continuous streams of Data. Updating the model in real time has huge potential in many of the real world scenarios can impact Businesses. Many of the existing complex real time machine learning methods only rely on Incremental learning techniques limiting the true potential of Real time learning (decremental learning, Parallel processing, Real time Feature selection and deletion etc.,). ART ML method can enhance the real time learning by giving all kind of flexibilities for incremental and decremental learning. This blog post explains how ART-ML library can be used for real time learning and its different functions.
Lastly, if you want to skip all this and just see all the code, feel free to give it a look on Github
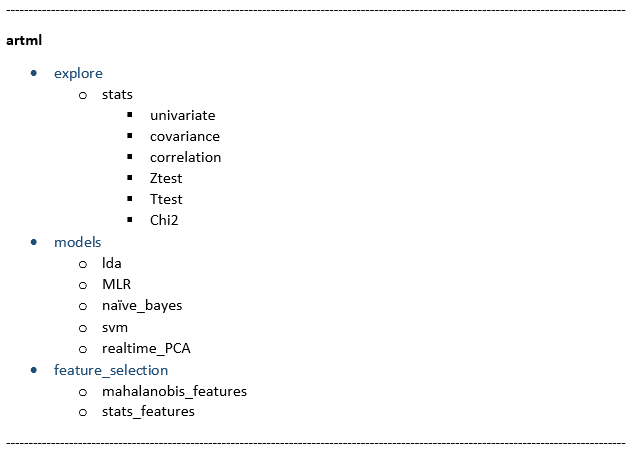
ART-ML library structure:
This is the basic API reference for artml library. For more details and for class & function reference please refer to Github source-code
ART-ML explanation with Iris Dataset:
The Iris dataset is one of the traditional datasets used for understanding machine learning concepts. Contained data has been collected in the early 20th century regarding characteristics of three different types of iris flowers. The famous Iris database is first used by Sir R.A Fisher and it is perhaps the best known database to be found in the pattern recognition literature.
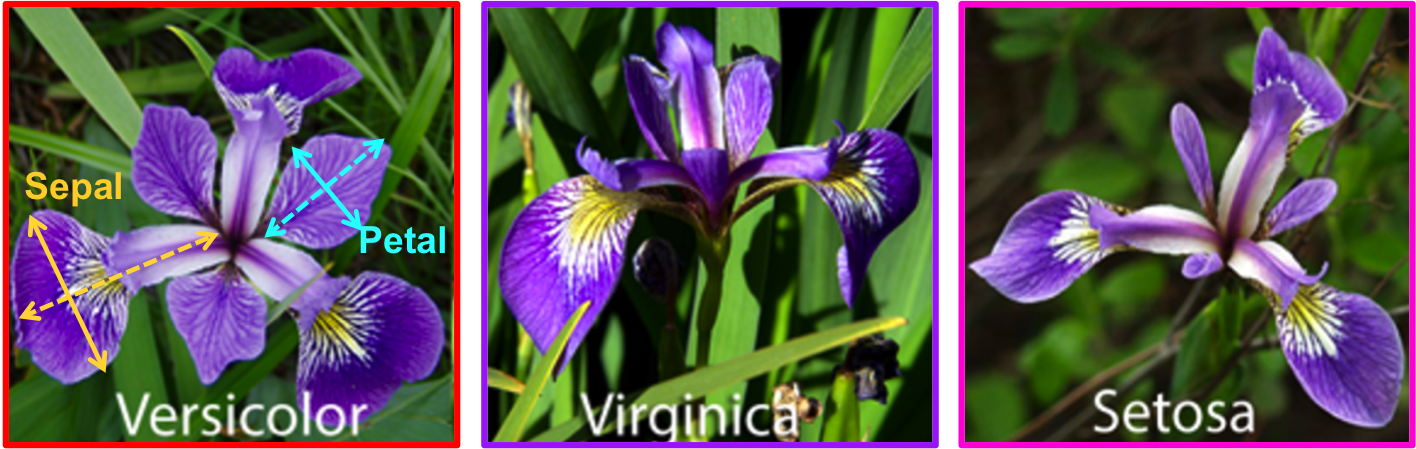

The data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a type of iris plant. One class is linearly separable from the other 2; the latter are NOT linearly separable from each other.
Although, real time learning is not required for Iris dataset, Iris being a well-used dataset in Machine learning family, this classic dataset is used to explain the ART-ML library and different features in ART-ML.
Let’s start by importing some libraries and examining the data.
Data Preparation
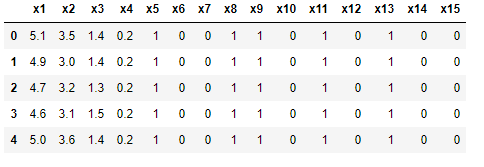
Since Iris dataset is having only 4 numerical and 1 categorical features, to expand the scope of dataset for analysis, dataset is transformed as given below. Categorical variables are encoded and binning of numerical features is done and this transformed iris dataset is used for explaining different ART-ML features.

Generating BET
As a first step in Adaptive real time learning, we create a Basic Element table which summarizes the whole dataset and can be updated in real-time by only using the newly generated data. BET is key for using ART-ML.
Here the Iris Dataset is split into two parts to explain the power of ART-ML library and how real time learning works.

Learn with Data
Using BET generated from the data we can create the models and also perform univariate and Bivariate exploration. If we want to update and learn from data streams, we need to update everything with the total data available at that time if we are using traditional methods. Since we are using BET here, If we update the BET itself only using the new data instead of using whole dataset we can update all other steps in real time.
Learn function is used to update the Basic Element Table with the new data. Since all the exploration steps and algorithms are built using the BET table. Whenever the BET is updated all other modeling steps get updated in real time with new data.

Real Time Exploration:
Univariate Statistics:
univariate function generates descriptive statistics that summarize the central tendency, dispersion and shape of a dataset’s distribution. univariate function in ART-Ml is equivalent to df.describe() in pandas. But in this case Univariate stats can be updated in real time.



Statistical tests
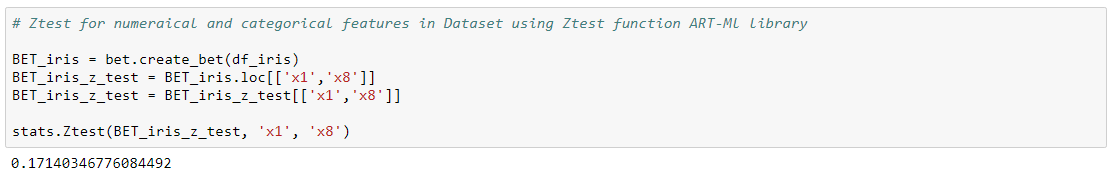
Z-test and t-test are basically the same. They assess whether the averages of two groups are statistically different from each other or not. This analysis is appropriate for comparing the averages of a numerical variable for two categories of a categorical variable. Ztest and Ttest functions can be used for performing these Statistical tests
Chi-square Test
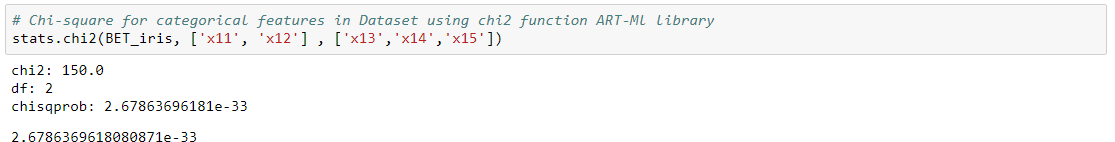
The chi-square test can be used to determine the association between categorical variables. It is based on the difference between the expected frequencies (e) and the observed frequencies (n) in one or more categories in the frequency table. The chi-square distribution returns a probability for the computed chi-square and the degree of freedom. A probability of zero shows a complete dependency between two categorical variables and a probability of one means that two categorical variables are completely independent.
chi2 function is used for checking the association between categorical variables in real time.
Real time Algorithms
Once we have BET, we can use all the traditional linear algorithms that are built in ART-ML library for making predictions. Whenever BET gets updated with the streaming Data, All the below models get updated in real time which improves the prediction accuracies and generates better Business insights for the real world case studies.
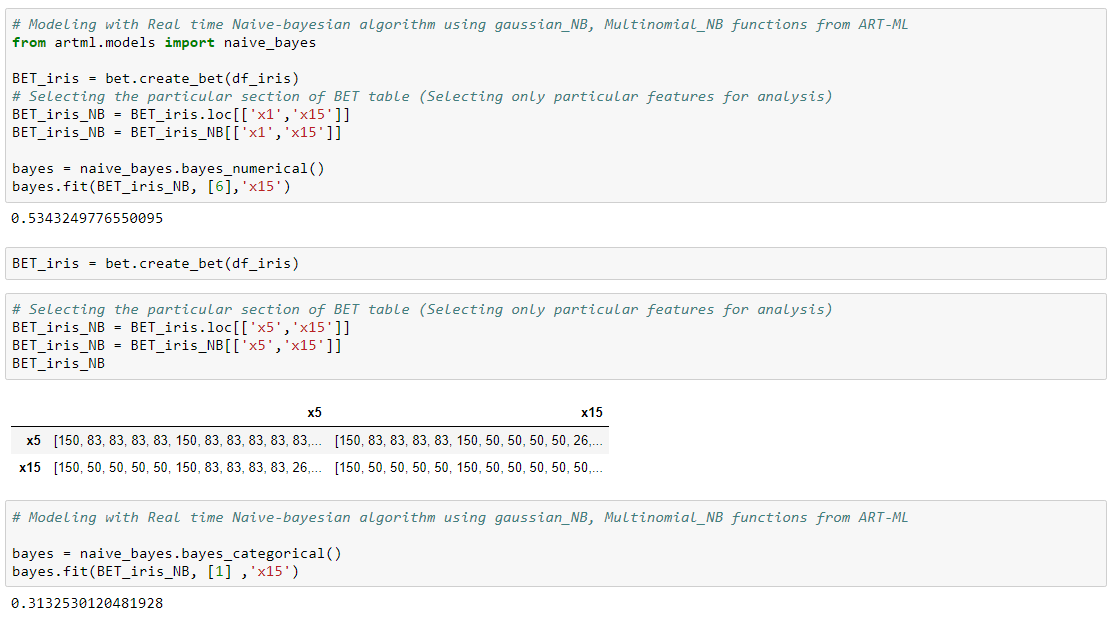
Naive Bayesian
In the real time version of Bayesian classifiers, we calculate the likelihood and the prior probabilities from the Basic Elements Table (BET) which can be updated in real time with the new data.
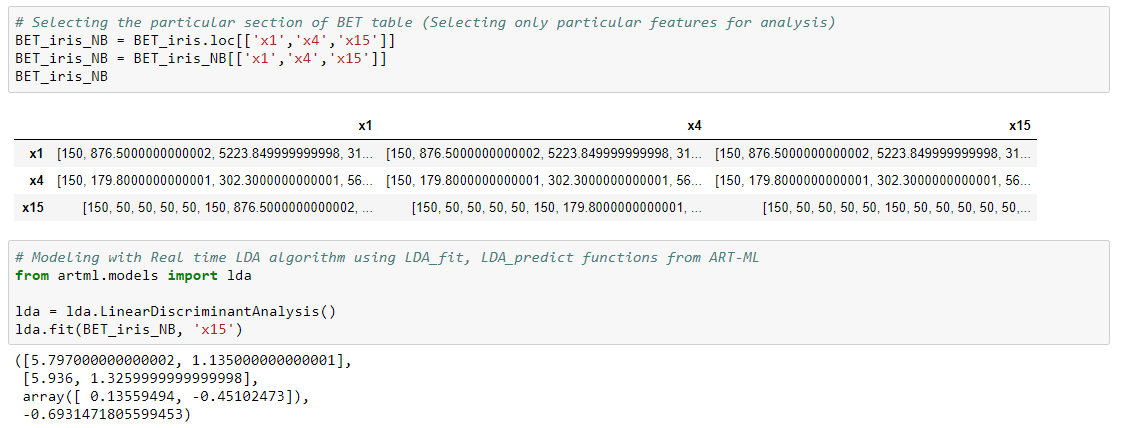
LDA
Real time Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) classification can be performed using the pooled covariance matrix (𝑪 ) derived from the BET table. Use LDA-fit and predict functions for fittiing the algorithm and classifying with new data.
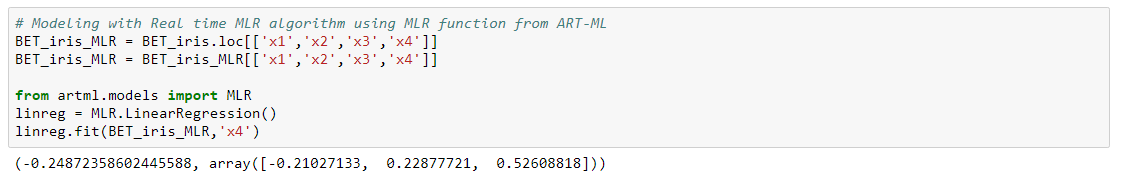
MLR
Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) is a method used to model the linear relationship between a target (dependent variable) and one or more attributes (independent variables).Real time MLR is built using real time covariance matrices.
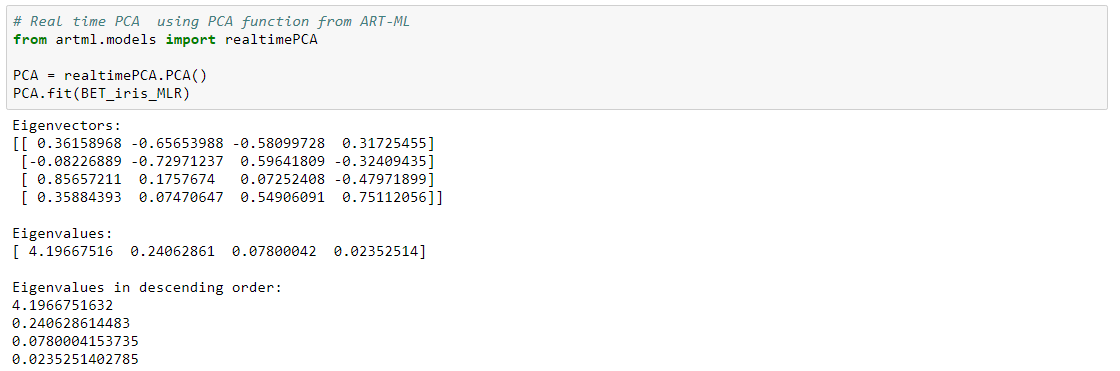
PCA
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a classical statistical method. This linear transform has been widely used in data analysis and data compression. The principal components (Eigenvectors) for a dataset can directly be extracted from the covariance matrix.
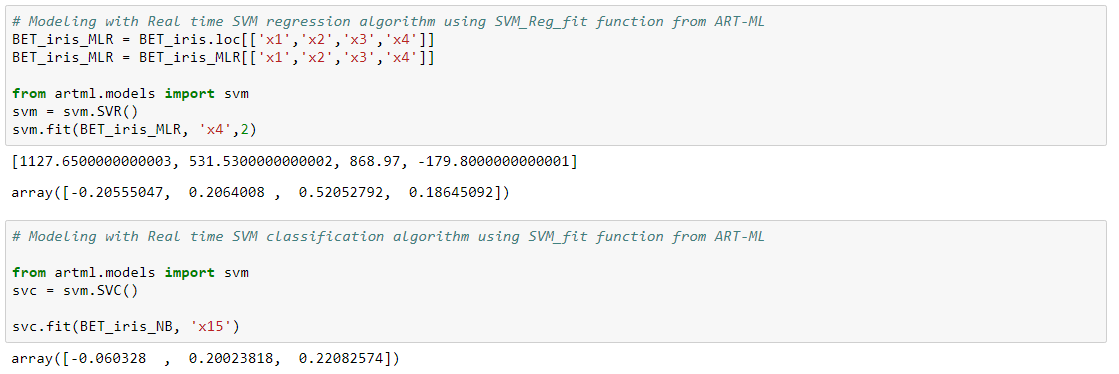
SVM Algorithm
SVM algorithm in Real time can be performed by using Linear Proximal SVM Algorithm defined by Fung and Mangasarian. Use SVM_Reg_fit for SVM regression and SVM_fit for SVM classification.
That’s it! Thanks for reading. In further posts real world datasets and case studies are explored where ART-ML can significantly impact traditional approaches and generate insights that have true Business value.