Adaptive Real time Algorithms
In many of the real life cases ongoing training is needed in machine learning models. This continues training of model in real time helps to give more useful Business insights and make better predictions.
Adaptive Real time machine Learning (ART-ML) can update models in real time with the incoming streaming data and can offer a real competitive advantage for organizations by making predictions better every time.
In this post, we take a tour of the Adaptive Real time machine learning algorithms and how they can be implemented using ART-ML library.
ART-ML technique can be applied for all the linear regression and classification algorithms like MLR, Naïve Bayesian, LDA, PCA etc.,
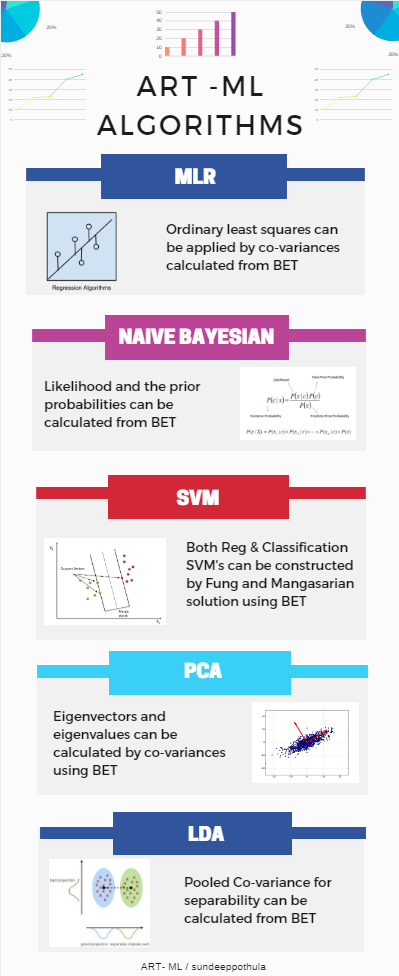
Multiple Linear Regression
MLR is based on ordinary least squares (OLS), the regression model is fit such that the sum-of-squares of differences of observed and predicted values (error) is minimized.
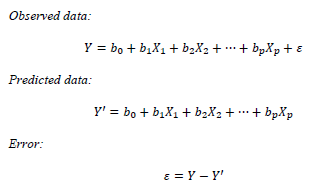
Coefficients for the linear equation can be found from the covariance matrix calculated from BET.
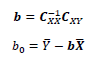
Naïve Bayesian
The Naïve Bayesian classifier is based on Bayes’ theorem with independence assumptions between attributes.
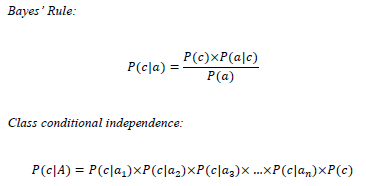
In the real time version of Bayesian classifiers, we calculate the likelihood and the prior probabilities from the Basic Elements Table (BET) which can be updated in real time. And for the numerical attributes likelihood can be calculated from the normal distribution equation. ART-ML library offers Bayesian functions for both categorical and numerical attributes.
Linear Support Vector Machine
Support Vector Machine (SVM) performs classification by finding the hyperplane that maximizes the margin between the two classes. Our implementation of the Real Time LSVM is based on Fung and Mangasarian solution.

Typically, v is chosen by means of a tuning (validating) set. And the two main components of the proximal LSVM equation (𝑬′𝑬 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑬′𝑫𝒆) can directly be extracted from the Basic Elements Table (BET). ART-ML library offers functions for both SVM classification and SVM regression.
Linear Discriminant Analysis
LDA is based upon the concept of searching for a linear combination of attributes that best separates two classes (0 and 1) of a binary attribute. To capture the notion of separability, Fisher defined the following score function which reduces the means between the groups and increases variability between two groups.
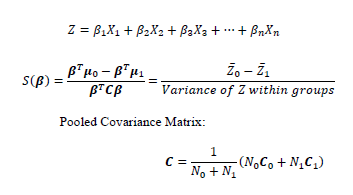
New data points to class 1 can be classified using the equation,
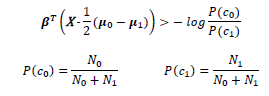
ART-ML library offers functions for all these things and the LDA model can be updated in real time using BET. This simple, mathematically robust model often produces accuracies as good as more complex methods for classification.
Principal Components Analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a classical statistical method. This linear transform has been widely used in data analysis and data compression. The principal components (Eigenvectors) for a dataset can directly be extracted from the covariance matrix. By sorting the eigenvectors in the order of descending eigenvalues, we can find directions in which the data has the most significant amounts of its variation. Real time PCA can be done by updating BET which further updates eigen values and eigen vectors.
This post gives overview of basic algorithms that can be implemented in Real time using ART-ML library. Check the ART- ML documentation for detailed description of these algorithms in real time.
Although, ART-Ml models are linear when used correctly they give better predictions and since we are training the models in real time with the continues streams of data they get better evert time. The real power of ART-ML lies in applying these algorithms in real world cases combined with the feature engineering.