Real time data exploration
In the Big Data world Exploring data is a prerequisite to analyzing data. Without proper exploration we could potentially use the wrong data and lead to non-optimal conclusions. Since the scope of datasets is very large, data exploration also brings important aspects of the data into focus for further analysis.
Real time Data Exploration can be catogarized into two types:
- Real time Univariate Data Exploration
- Real time Bivariate Data Exploration
Real time Univariate Data Exploration:
Univariate analysis explores variables (attributes) one by one by summarizing each attribute using statistical techniques.
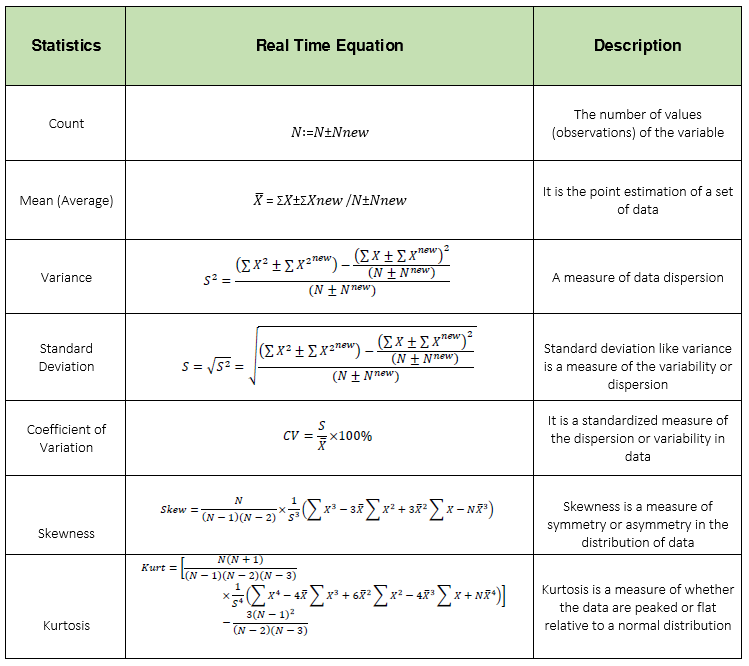
Mode, median cannot be transformed to real time. However,they can be approximated by having the discretized (binned) version of a numerical attribute. Eg: When numerical attributes are discretized in bins, the mode is defined as the bin where most observations lie.
Minimum and Maximum can be updated in real time incrementally but not decrementally. It means if we lose an existing maximum or minimum value we would need to consider all historical data to replace them. One practical option is using the lower bound (minimum) and upper bound (maximum) of the discretized version of a numerical attribute.
Real time Bivariate Data Exploration:
Bivariate data analysis is the simultaneous analysis of two attributes (variables). It explores the concept of relationship between two attributes, whether there is an association and the strength of this association, or whether there are differences between two attributes and the significance of these differences.
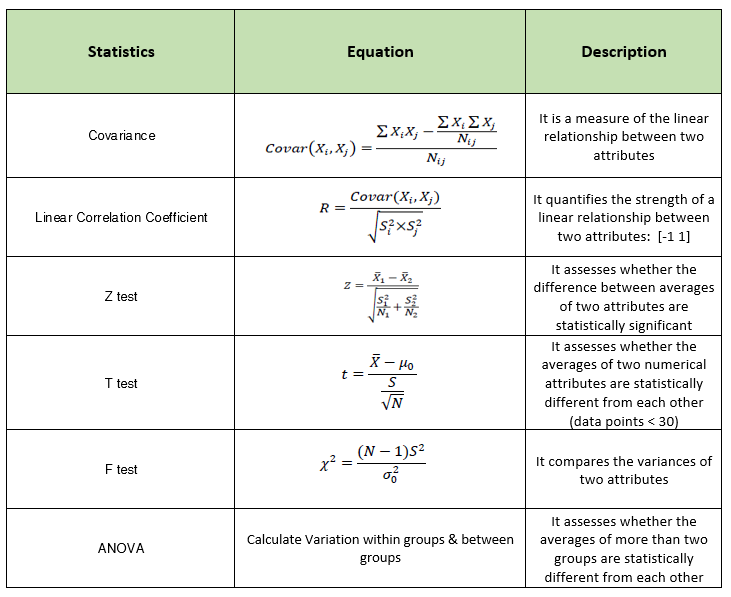
Many of the bivariate statistics like Z test, T test, Anova etc. rely on the conditional univariate statistics.These define univariate statistics for an attribute 𝑋𝑖 given a binary attribute 𝑋𝑗 when 𝑋𝑗=1. All the conditional univariate statistics can be calculated by the Real time equations using Basic Element Table (BET). Check GITHUB for python code of each of these functions.