Generating BET in Python
Basic element table is the key for all the steps in Adaptive real time machine learning(ART-ML) technique. Although, there is no particular data structure and process that needs to be used for generating BET, this example explains one of the methods to generate BET in an Atomic level.
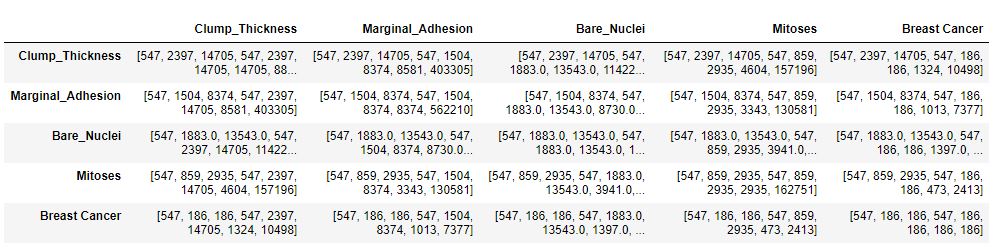
Here, BET is stored in the form of a square Matrix (N*N) where N is number of features.Below python code shows how BET can be generated in layman form in the most atomic level:
def BET(df):
col = df.columns
col = col.tolist()
l = len(col)
x ={}
for m in range(l):
for n in range(l):
x[m,n] = []
for i in range(l):
for j in range(l):
y=col[j]
z=col[i]
count_x = len(df[col[i]]) # count in particular X column
x[i,j].append(count_x)
sum_x = df[col[i]].sum() # Sum of elemensts in x
x[i,j].append(sum_x)
sum_x2 = (df[z]*df[z]).sum() # Sum of elemensts in x2
x[i,j].append(sum_x2)
count_y = len(df[col[j]]) # count in particular Y column
x[i,j].append(count_y)
sum_z = df[col[j]].sum() # Sum of elemensts in y
x[i,j].append(sum_z)
sum_z2 = (df[col[j]]*df[col[j]]).sum() # Sum of elemensts in y2
x[i,j].append(sum_z2)
sum_yz = (df[col[i]]*df[col[j]]).sum() # Sum of elemensts in xy
x[i,j].append(sum_yz)
sum_2yz = (df[col[i]]*df[col[j]]*df[col[i]]*df[col[j]]).sum() # Sum of elemensts in (xy)2
x[i,j].append(sum_2yz)
z={}
for m in range(l):
z[m] = []
for i in range(l):
for j in range(l):
z[i].append(x[j,i])
result = pd.DataFrame(z, index=col)
result.columns = col
return(result)After generating BET, this table can be used for Data exploration & for Modeling. To use this in real time, BET can be updated in real time using the real time equation for BET. As, BET is updated with the new Data, we can update the model in real time.
Updating BET in Real-Time:
BET has the flexibility to be modified with the new data in multiple ways as mentioned below.
- Incremental learning (Learn)
- Decremental learning (Forget)
- Attribute addition (Grow)
- Attribute deletion (Shrink)
This gives us flexibility for on the fly attribute addition or deletion to update the models. Check GITHUB for python code of each of these functions.